by Maria Popova
“The act of writing is an integral part of my mental life; ideas emerge, are shaped, in the act of writing… a special, indispensable form of talking to myself.”
 Who we are and who we become is in large part the combinatorial product of the people and ideas we surround ourselves with — what William Gibson so memorably termed our“personal micro-culture” and Brian Eno called“scenius.” The more different those people are from us, the more they expand the echo chamber of our own mind, the more layered and beautiful the symphony of the spirit becomes. Nowhere is this self-expansion via relationship more evident than in the friendships between great artists and great scientists, one of the most heartening examples of which is the friendship between legendary neurologist Oliver Sacks and the poet Thom Gunn.
Who we are and who we become is in large part the combinatorial product of the people and ideas we surround ourselves with — what William Gibson so memorably termed our“personal micro-culture” and Brian Eno called“scenius.” The more different those people are from us, the more they expand the echo chamber of our own mind, the more layered and beautiful the symphony of the spirit becomes. Nowhere is this self-expansion via relationship more evident than in the friendships between great artists and great scientists, one of the most heartening examples of which is the friendship between legendary neurologist Oliver Sacks and the poet Thom Gunn.
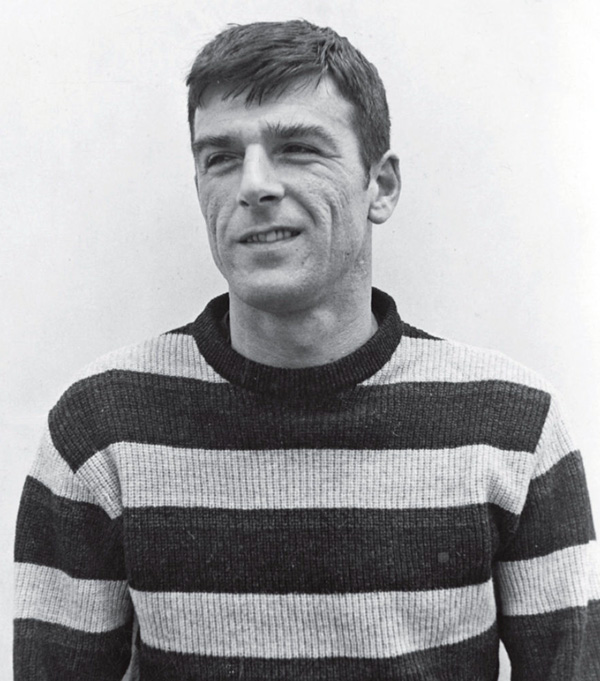
Thom Gunn in the early 1960s, around the time Dr. Sacks met him (Courtesy of Oliver Sacks)
To be sure, Sacks’s love affair with writing predates his meeting Gunn and even his foray into science. Nicknamed Inky as a boy for his voracious appetite for pen and paper, which covered everything in ink, he began journaling at an early age — a formative practice of learning to think on paper and converse with himself. Joining the extensive roster of celebrated writers who championed the creative benefits of keeping a diary and speaking to the potency of journaling as an antidote to Tom Waits’s complaint about the inopportune timing of the muse, Sacks writes:
I started keeping journals when I was fourteen and at last count had nearly a thousand. They come in all shapes and sizes, from little pocket ones which I carry around with me to enormous tomes. I always keep a notebook by my bedside, for dreams as well as nighttime thoughts, and I try to have one by the swimming pool or the lakeside or the seashore; swimming too is very productive of thoughts which I must write, especially if they present themselves, as they sometimes do, in the form of whole sentences or paragraphs…
But for the most part, I rarely look at the journals I have kept for the greater part of a lifetime. The act of writing is itself enough; it serves to clarify my thoughts and feelings. The act of writing is an integral part of my mental life; ideas emerge, are shaped, in the act of writing.
My journals are not written for others, nor do I usually look at them myself, but they are a special, indispensable form of talking to myself.
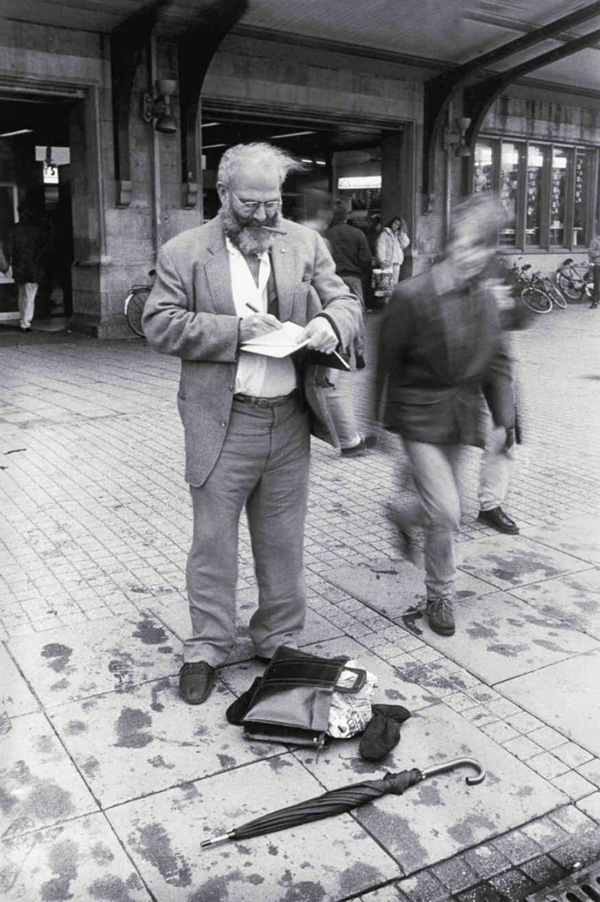
Dr. Sacks captures a thought in his journal at Amsterdam's busy train station (Photograph: Lowell Handler)
He adds:
The need to think on paper is not confined to notebooks. It spreads onto the backs of envelopes, menus, whatever scraps of paper are at hand. And I often transcribe quotations I like, writing or typing them on pieces of brightly colored paper and pinning them to a bulletin board.
What Sacks is describing is akin to a commonplace book — that Medieval Tumblr in which thinkers recorded quotations and ideas from whatever they were reading, assembling a personal archive of the ideas that shaped their own minds. (Brain Pickings is essentially one giant commonplace book, and this very piece a sort of bulletin board pinned to which is my discourse with Sacks’s extraordinary text.)
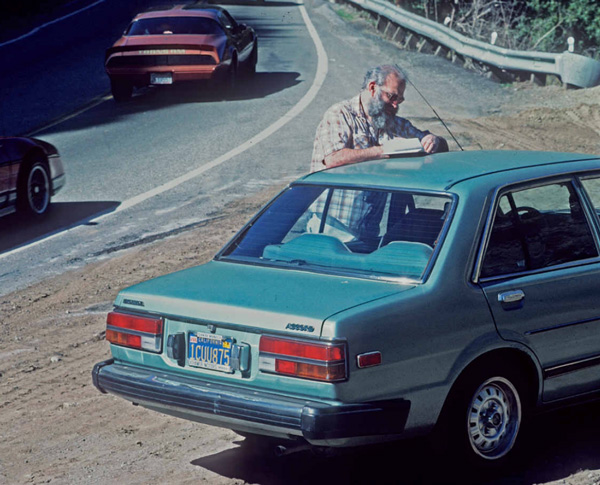
Another thought recorded atop a car roof on the side of the road (Courtesy of Oliver Sacks)
By the time he was in graduate school, Sacks began externalizing these inner conversations, doing for others what he had been doing for himself on the pages of his journals — clarifying the complexities of mental life at the intersection of science and storytelling, honing the singular gift for which he is so beloved today.
He was so electrified by working with patients at a migraine clinic in the mid-1960s that he felt compelled to transmute these insights into a book. But when he finally finished the manuscript and showed it to his boss at the clinic — a prominent but petty and egomaniacal neurologist by the name of Arnold P. Friedman — he was curtly told that the manuscript was garbage, that he had to destroy it, and that he dare not think about turning it into a book ever again; or else, Friedman threatened, Sacks would be promptly fired and barred from getting another job anywhere in America. Friedman confiscated the manuscript and locked it away.
Still, Sacks trusted that he had written something substantive and important — something that might forever change our understanding of how the mind works. He suppressed his feelings for months but, finally, the resentment exploded into action: One night, with the help of the clinic’s janitor, he sneaked in and, between midnight and 3 A.M., arduously copied his own notes by hand. The next day, he told Friedman he was taking a long leave to London and when his boss demanded a reason, Sacks responded that he had no choice but to write the forbidden book.
He was fired via telegram a week later. And yet a strange sense of liberation set in, which he poured into the writing.
But if this wasn’t courageous enough an act, he soon performed what is perhaps the greatest act of creative courage — the same one John Steinbeck had performed three decades earlier in destroying a manuscript he didn’t feel was good enough and rewriting it from scratch into what would become his Pulitzer-winning novel The Grapes of Wrath, the cornerstone of his Nobel Prize. Sacks recounts:
I was dissatisfied with my 1967 manuscript and decided to rewrite the book. It was the first of September, and I said to myself, “If I do not have the finished manuscript in Faber’s hands by September 10, I shall have to kill myself.” And under this threat, I started writing. Within a day or so, the feeling of threat had disappeared, and the joy of writing took over. I was no longer using drugs, but it was a time of extraordinary elation and energy. It seemed to me almost as though the book were being dictated, everything organizing itself swiftly and automatically. I would sleep for just a couple of hours a night. And a day ahead of schedule, on September 9, I took the book to Faber & Faber. Their offices were in Great Russell Street, near the British Museum, and after dropping off the manuscript, I walked over to the museum. Looking at artifacts there — pottery, sculptures, tools, and especially books and manuscripts, which had long outlived their creators — I had the feeling that I, too, had produced something. Something modest, perhaps, but with a reality and existence of its own, something that might live on after I was gone.
I have never had such a strong feeling, a feeling of having made something real and of some value, as I did with that first book, which was written in the face of such threats from Friedman and, for that matter, from myself. Returning to New York, I felt a sense of joyousness and almost blessedness. I wanted to shout, “Hallelujah!” but I was too shy. Instead, I went to concerts every night — Mozart operas and Fischer-Dieskau singing Schubert — feeling exuberant and alive.
Sacks’s jubilant intuition wasn’t misplaced — that manuscript became his 1970 debut Migraine, which was welcomed with wholehearted critical acclaim and catapulted him into the status of masterful science storyteller. When the book came out, he found out that Friedman had adapted the original manuscript and attempted to publish it under his own name — a tragicomic testament to the fact that it is Sacks’s singular gift as a writer and storyteller, not his scientific genius alone, that make him the cultural icon he is today.
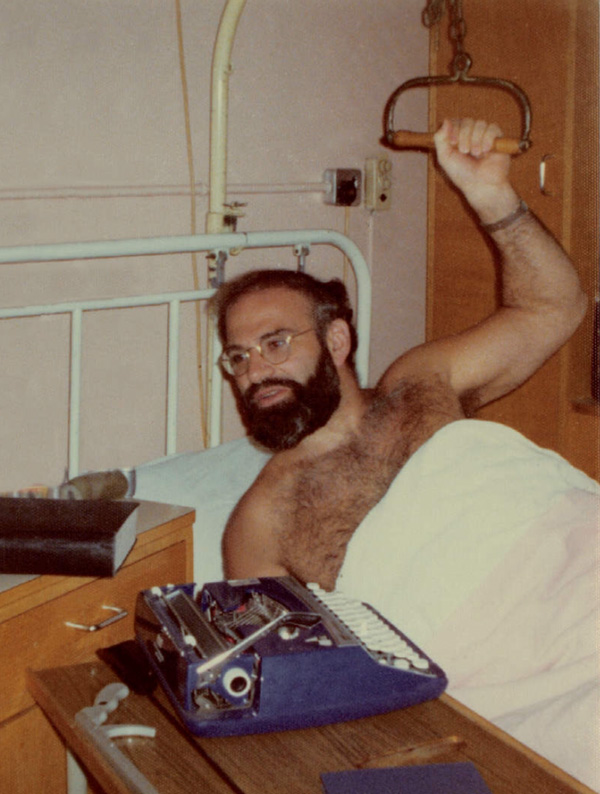
Dr. Sacks recovering in the hospital with nothing but a typewriter by his side. He had broken his leg in Norway, falling down a slippery canyon while being chased by a bull. (Courtesy of Oliver Sacks)
Sacks had befriended Thom Gunn in the early 1960s, but it wasn’t until after the publication of Migraine that he was able to engage with the poet in conversations about writing more confidently — a confidence further nurtured by Gunn’s encouraging feedback which, alongside the staunch support of Sacks’s beloved aunt Lennie, was instrumental in emboldening the budding writer to embark upon this far from easy path.
He talked with Gunn about “the process of writing, the rushes and stoppages, the illuminations and darknesses, which seemed to be part and parcel of the creative process.” Long before cognitive scientists came to study the psychology of writing, Gunn captured the mysterious psychological messiness of the process in one of his letters to Sacks:
I am a bit slothful at the moment. My pattern seems to be: a long cessation of any coherent writing after I have completed a MS, then a tentative start followed by, during the next few years, various separate bursts of activity, ending with a sense of the new book as a whole, in which I make discoveries about my subject(s) that I have never anticipated. It’s strange, the psychology of being a writer. But I suppose it’s better not to be merely facile — the blocks, the feelings of paralysis, the time when language itself seems dead, these all help me in the end, I think, because when the “quickenings” do come they are all the more energetic by contrast.
Sacks reflects on the sincerity of his friend’s values:
It was crucial for Thom that his time be his own; his poetry could not be hurried but had to emerge in its own way… “My income,” [he] wrote, “averages about half that of a local bus-driver or street sweeper, but it is of my own choosing, since I prefer leisure to working at a full-time job.” But I do not think Thom felt too constrained by his slender means; he had no extravagances (though he was generous with others) and seemed naturally frugal. (Things eased up in 1992, when he received a MacArthur Award, and after this he was able to travel more and enjoy some financial ease, to indulge himself a bit.)
I was particularly taken, and felt a deep kinship, with Sacks’s parenthetical note about Gunn’s ethos regarding writing about the writing of others:
Thom rarely reviewed what he did not like, and in general his reviews were written in the mode of appreciation.
Despite knowing his friend’s disposition toward criticism, Sacks recounts:
I sometimes felt terrified of his directness — terrified, in particular, that he would find my writings, such as they were, muzzy, dishonest, talentless, or worse.
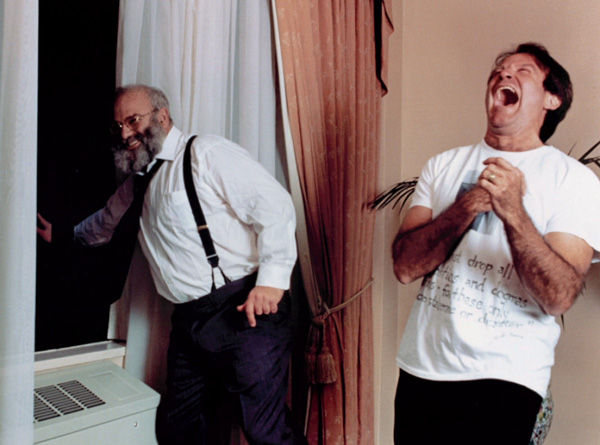
Dr. Sacks on the set of the cinematic adaptation of his book Awakenings, with Robin Williams, 1989 (Courtesy of Oliver Sacks)
But the feedback that most touched him was about his 1973 book Awakenings — a cultural classic that was eventually made into a film starring Robin Williams as Sacks. Gunn wrote:
Awakenings is, anyway, extraordinary. I remember when, some time in the late Sixties, you described the kind of book you wanted to write, simultaneously a good scientific book and worth reading as a well-written book, and you have certainly done it here… I have also been thinking of the Great Diary you used to show me. I found you so talented, but so deficient in one quality — just the most important quality — call it humanity, or sympathy, or something like that. And, frankly, I despaired of your ever becoming a good writer, because I didn’t see how one could be taught such a quality… Your deficiency of sympathy made for a limitation of your observation… What I didn’t know was that the growth of sympathies is something frequently delayed till one’s thirties. What was deficient in these writings is now the supreme organizer of Awakenings, and wonderfully so. It is literally the organizer of your style, too, and is what enables it to be so inclusive, so receptive, and so varied… I wonder if you know what happened. Simply working with the patients over so long, or the opening-up helped by acid, or really falling in love with someone (as opposed to being infatuated). Or all three…
Sacks adds:
I was thrilled by this letter, a bit obsessed, too. I did not know how to answer Thom’s question. I had fallen in love — and out of love — and, in a sense, was in love with my patients (the sort of love, or sympathy, which makes one clear-eyed).
I loved the sense of history, of predecessors, in many of Thom’s poems. Sometimes this was explicit, as in his “Poem After Chaucer” (which he sent me as a New Year’s card in 1971); more often it was implicit. It made me feel at times that Thom was a Chaucer, a Donne, a Lord Herbert, who now found himself in the America, the San Francisco, of the late twentieth century. This sense of ancestors, of predecessors, was an essential part of his work, and he often alluded to, or borrowed from, other poets and other sources. There was no tiresome insistence on “originality,” and yet, of course, everything he used was transmuted in the process.
I must count my writing as an essential part of the way in which I deal with life. I am however a rather derivative poet. I learn what I can from whom I can. I borrow heavily from my reading, because I take my reading seriously. It is part of my total experience and I base most of my poetry on my experience. I do not apologize for being derivative… It has not been of primary interest to develop a unique poetic personality, and I rejoice in Eliot’s lovely remark that art is the escape from personality.
Dr. Sacks at home on City Island, the Bronx (Courtesy of Oliver Sacks)
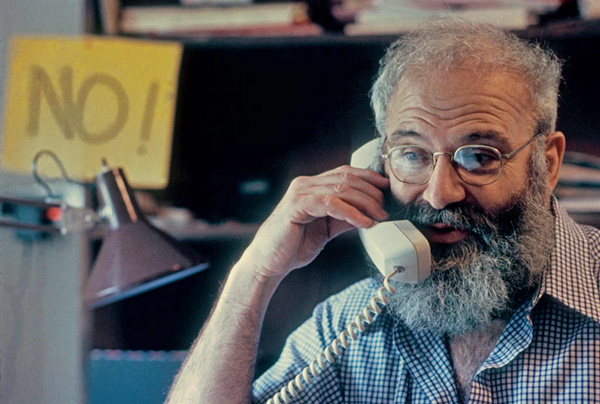
And yet art requires undisturbed personal space for the “quickenings” of the creative process to unfold slowly — something Sacks protected with great discipline as he blossomed into a prolific writer himself. In his house on City Island, he tacked a sign to the wall above his desk that simply read “NO!” — “reminding myself to say no to invitations so I could preserve writing time,” he explains. It is no accident that Sacks dedicates the final sentences in his autobiography to this great love of writing and, in a sentiment that calls to mindthe psychology of flow, fuses it with his great gift for science:
I am a storyteller, for better and for worse.
I suspect that a feeling for stories, for narrative, is a universal human disposition, going with our powers of language, consciousness of self, and autobiographical memory.
The act of writing, when it goes well, gives me a pleasure, a joy, unlike any other. It takes me to another place — irrespective of my subject — where I am totally absorbed and oblivious to distracting thoughts, worries, preoccupations, or indeed the passage of time. In those rare, heavenly states of mind, I may write nonstop until I can no longer see the paper. Only then do I realize that evening has come and that I have been writing all day.
Over a lifetime, I have written millions of words, but the act of writing seems as fresh, and as much fun, as when I started it nearly seventy years ago.
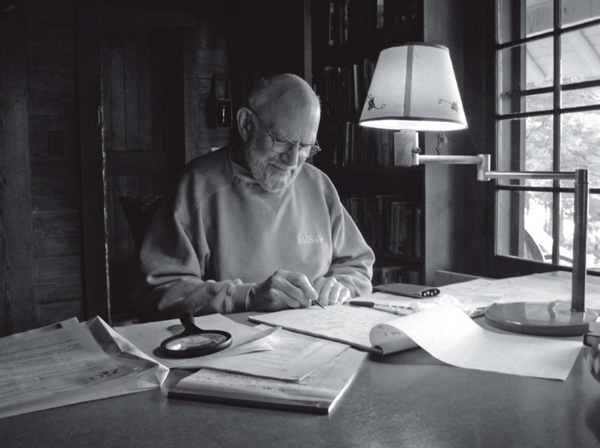
Oliver Sacks writing in his seventies (Photograph: Bill Hayes)
Every page of the altogether magnificent On the Move emanates this contagious delight in writing and furnishes an equivalent delight in reading — a sense of being invited, in the most generous way possible, into a lifetime of Sacks’s conversations with his own luminous, incessantly quickening mind. Take another step inside.
Donating = Loving
Bringing you (ad-free) Brain Pickings takes hundreds of hours each month. If you find any joy and stimulation here, please consider becoming a Supporting Member with a recurring monthly donation of your choosing, between a cup of tea and a good dinner.
You can also become a one-time patron with a single donation in any amount.
 Brain Pickings has a free weekly newsletter. It comes out on Sundays and offers the week’s best articles. Here’s what to expect. Like? Sign up.
Brain Pickings has a free weekly newsletter. It comes out on Sundays and offers the week’s best articles. Here’s what to expect. Like? Sign up.